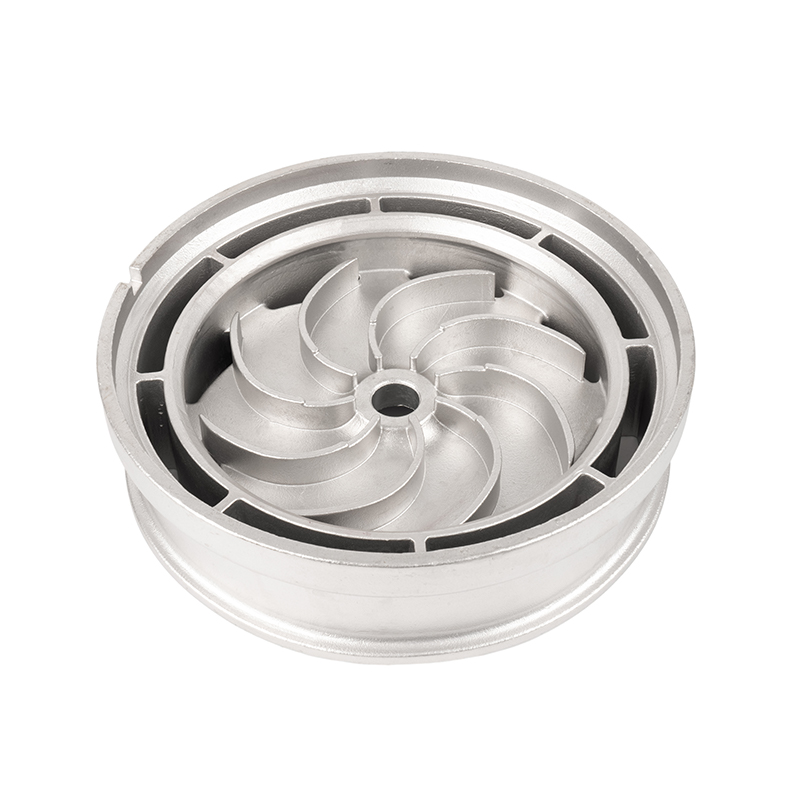
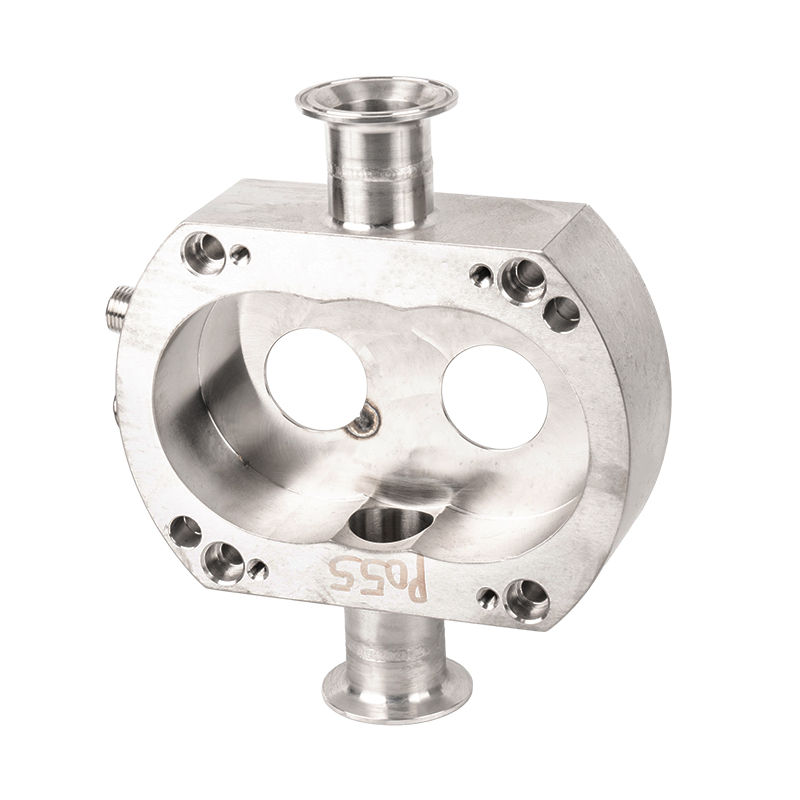
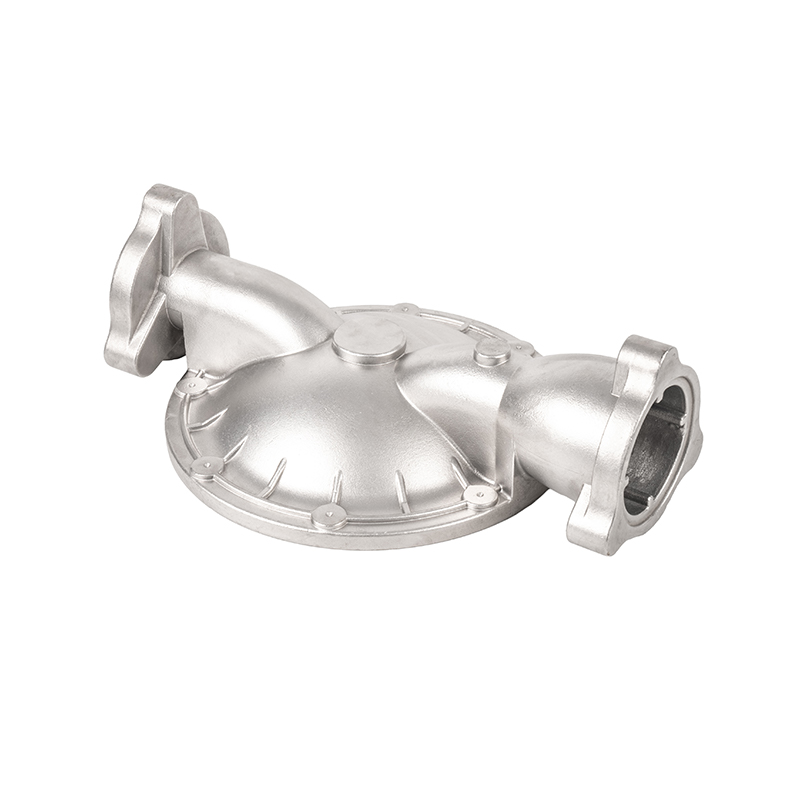
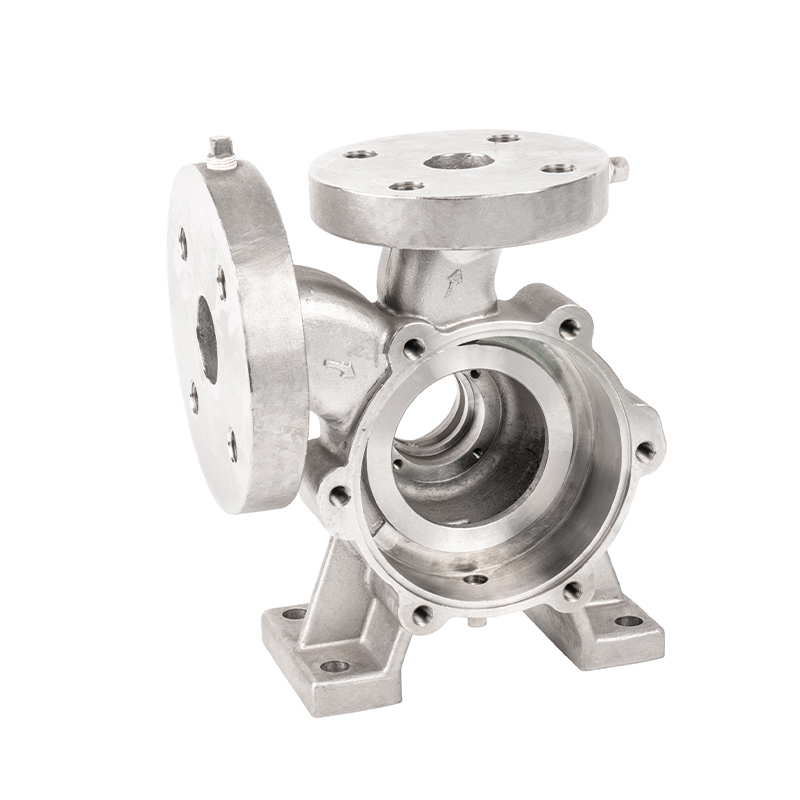
The precision casting process of water pump castings
Water pump castings are key components in the water pump industry. Precision casting is a commonly used process in its manufacturing process. Precision casting can produce water pump castings with complex shapes and precise dimensions by using precision molds and advanced production technology.
Precision casting is a high-precision, high-quality casting process, and its process flow includes mold preparation, wax injection molding, sintering, pouring, cooling, dewaxing and post-processing.
Mold preparation is the first step in precision casting. According to the shape and size requirements of water pump castings, precision molds are made. Precision molds are usually made of metal materials with high precision and high temperature resistance. The mold can be divided into an upper mold and a lower mold, and a cavity is formed between the upper and lower molds for injection molding of wax molds.
Wax injection molding is the second step in precision casting. The molten wax is injected into the mold, and the wax mold is taken out after the wax material cools and solidifies. The preparation of the wax mold requires controlling the temperature and speed of injection molding to ensure the accuracy and surface quality of the wax mold. During the preparation of the wax mold, gates and risers can be added to the wax mold for subsequent pouring and dewaxing.
Sintering is the third step in precision casting. The wax model is placed in a high-temperature furnace for sintering. The purpose of sintering is to pyrolyze the wax model, melt it and flow out to form a cavity. During the sintering process, the temperature and time need to be controlled to ensure that the wax model is completely sintered, while avoiding overburning and causing the surface of the casting to be rough.
Pouring is the fourth step of precision casting. After the metal material is melted, it is poured into the sintered wax model. The pouring process needs to control the temperature and fluidity of the casting to avoid pores and defects inside the casting. In order to ensure the smooth pouring, gates and risers are usually set on the wax model. The gate is used to pour the molten metal, and the riser is used to discharge the gas and metal slag in the sintered wax mold.
Cooling is the fifth step of precision casting. After the metal cools and solidifies, the casting is taken out. The cooling time depends on the size and material of the casting, and it usually takes some time to cool completely. During the cooling process, the metal changes from liquid to solid and gradually forms the desired casting shape.
Dewaxing is the sixth step of precision casting. The cooled casting is placed in a dewaxing furnace for dewaxing. The purpose of dewaxing is to completely remove the residue in the sintered wax mold for subsequent sintering and post-processing. During the dewaxing process, the temperature and time need to be controlled to avoid sintering on the surface of the casting.
Post-processing is the last step of precision casting. The casting is trimmed, cleaned and surface treated. Trimming includes removing burrs and excess material on the casting, cleaning includes removing dewaxing residues and cleaning the surface of the casting, and surface treatment includes polishing, painting, etc. The purpose of post-processing is to make the casting achieve the required dimensional accuracy and surface quality.


 English
English Español
Español русский
русский 中文简体
中文简体